| HOME | HELP | FEEDBACK | SUBSCRIPTIONS | ARCHIVE | SEARCH | TABLE OF CONTENTS |
|---|
|
|
||||||||
a University of Houston-Clear Lake, Houston, Texas.
b Texas A&M University, College Station, Texas (retired)
Terry L. Dupler, Fitness and Human Performance Laboratory, University of Houston-Clear Lake, 2700 Bay Area Blvd., Houston, TX 77058 E-mail: dupler{at}cl.uh.edu.
Decision Editor: William B. Ershler, MD
Background. The purpose of this study was to develop and validate anthropometric body composition prediction equations for elderly (i.e.,  65 years old) men. This was necessary because of a lack of accurate and reliable predictive equations specifically developed for this population.
65 years old) men. This was necessary because of a lack of accurate and reliable predictive equations specifically developed for this population.
Methods. Seventy-five elderly men were randomly assigned to either an equation development sample (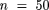 ) or an equation validation sample (
) or an equation validation sample (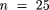 ). Subject anthropometric measures were analyzed in a regression procedure with hydrodensitometry-determined body density, percentage of fat, fat-free mass, and fat weight to develop prediction equations for each body composition variable. The equation estimates were then validated against the hydrostatically determined measures.
). Subject anthropometric measures were analyzed in a regression procedure with hydrodensitometry-determined body density, percentage of fat, fat-free mass, and fat weight to develop prediction equations for each body composition variable. The equation estimates were then validated against the hydrostatically determined measures.
Results. Four equations were developed and validated for the estimation of elderly male body composition variables [one each for body density (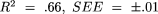 , where SEE is the standard error of estimate), percentage of fat (
, where SEE is the standard error of estimate), percentage of fat (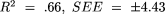 ), fat-free mass (
), fat-free mass (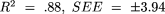 , and fat weight (R
, and fat weight (R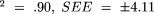 )]. The equations provided estimates of body density, percentage of fat, fat-free mass, and fat weight, which were not statistically different from the hydrostatically determined criterion variables.
)]. The equations provided estimates of body density, percentage of fat, fat-free mass, and fat weight, which were not statistically different from the hydrostatically determined criterion variables.
Conclusions. The results of this study indicate that accurate and reliable anthropometric predictive equations can be developed for an active and healthy elderly male population. These equations may be used for accurate epidemiological testing of this group's body composition variables.
| HOME | HELP | FEEDBACK | SUBSCRIPTIONS | ARCHIVE | SEARCH | TABLE OF CONTENTS |
|---|
| All GSA journals | The Gerontologist |
| Journals of Gerontology Series B: Psychological Sciences and Social Sciences | |